How Satellite Imagery Assists in Reforestation Strategies
Every year, around 10 million hectares of forest is stripped bare around the world, with only half of this deforested land offset by regrowth. This amount of deforestation can have dire effects in areas by altering weather patterns, destroying habitats and biodiversity loss.
In the face of increased deforestation, developing effective reforestation strategies is more crucial than ever. One innovative approach that has shown great promise is the use of high-resolution satellite imagery. This technology is revolutionising the way we understand and address deforestation, providing invaluable insights that can guide conservation efforts.
In this article, we’ll highlight the current challenges faced with reforestation and how satellite imagery assists in these efforts.
The Current Challenge with Reforestation.
Reforestation is a complex and extensive process that requires careful planning and execution. Current methods of reforestation is an expensive task, difficult to plan and even harder to execute. It often involves ground surveys to identify suitable areas for tree planting, a labour-intensive and time-consuming task.
Furthermore, monitoring the success of reforestation efforts is challenging, especially in remote areas. With projects having to monitor an entire forest over a number of years. Success is also subject to weather, pests and weeds as well as continued measurement of thousands of trees by hand. So how can we improve this? Well that’s where satellite imagery comes into play.

How Satellite Imagery Assists Reforestation Efforts
High-resolution satellite imagery offers a bird’s eye view of the Earth’s surface, capturing detailed images that can reveal a wealth of information. Using satellite imagery technology allows conservationists to identify deforested areas, monitor tree growth, and assess the health of restored forests.
In fact, with satellite imagery we can now effectively monitor large landscapes for changes in vegetation cover, track tree growth rates, and assess the overall success of reforestation initiatives with unprecedented detail and accuracy. Additionally, satellite imagery also offers detailed images with a GSD as small as 0.5m. This level of detail can provide crucial insights into the health and growth of restored forests, guiding future reforestation strategies as well as save time and cost that would normally be spent on surveyors and on site monitoring team.We can also compare and gain critical insights using an archive of high-res satellite imagery. Arlula’s Archive of satellite imagery enables you access to decades of high-res earth captures with multiple leading suppliers to enable you to to note any common trends and changes over time in a given area.
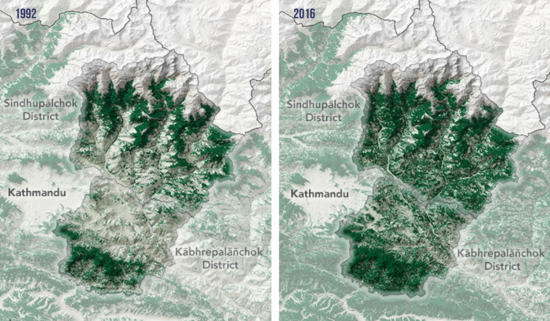
Besides using archive imagery to compare a forest’s landscape, satellite technology enables one to easily task near real-time imagery, further improving your monitoring capability. This is essential to not only observe areas but also further improve our understanding, but provides critical insight allowing teams to predict change and enhance response to any change. For example, monitoring water cycles is a key aspect in reforestation efforts. By utilising satellite technology, one is able to track any changes in water moisture, helping reforestation planners further optimise their strategies in restoring back these areas.
Many satellites are equipped with advanced sensors providing either multispectral or hyperspectral imagery. By using multispectral and hyperspectral, GIS scientists are able to compare different wavelengths and generate a vegetation index allowing further enhancement of monitoring capabilities.
Let’s look at a real life case of where satellite imagery helped assist in detecting deforestation as well as reforestation efforts.
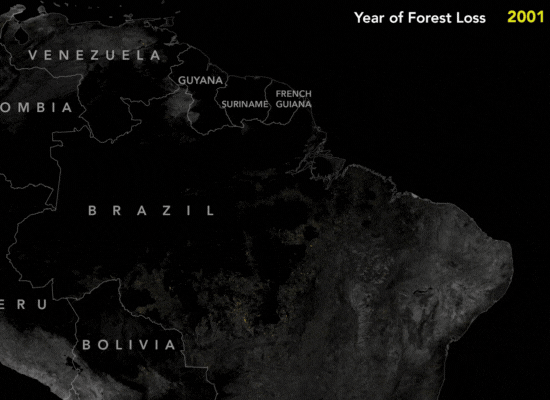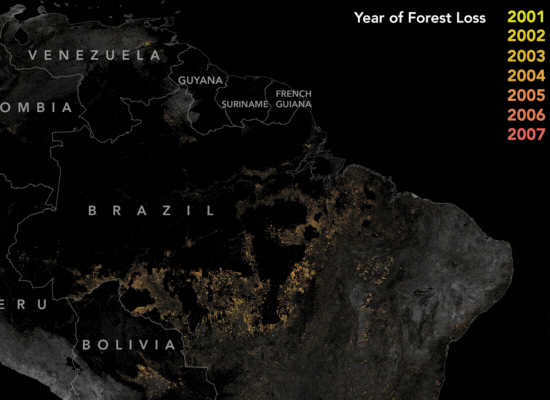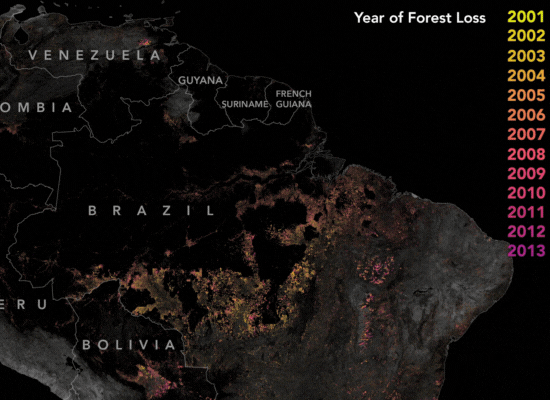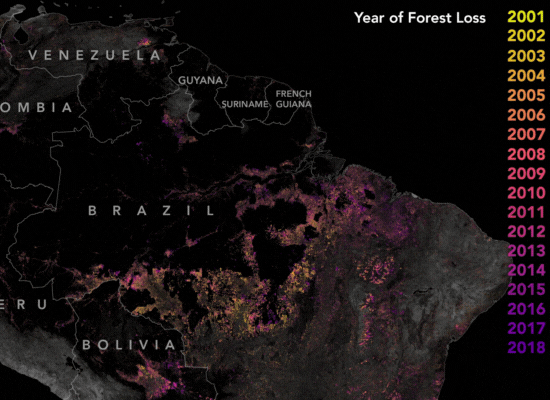
How Satellite Imagery Assists The Amazon
The Amazon rainforest is one of the largest and oldest rainforests to date, with a vast biodiversity with at least 40,000 plant species, 427 mammals. Over the years, extensive land clearing for various purposes posed a serious risk to the Amazon’s biodiversity and ecological balance. In 2004, the Brazilian government’s implementation of the Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Deforestation in the Legal Amazon (PPCDAm) marked a pivotal moment. This initiative not only established protected areas and indigenous territories but also employed satellite monitoring systems like PRODES and DETER to track deforestation trends in real-time.
These satellite-based monitoring systems played a crucial role in curbing deforestation by providing timely insights and enabling stakeholders to actively participate in conservation efforts. By offering transparency and rapid alerts, these technologies empowered enforcement agencies to promptly respond to deforestation activities, resulting in a significant reduction in large-scale clearings. By 2012, deforestation rates had dropped by nearly 80%, demonstrating the vital role of satellite technology in preserving the Amazon rainforest’s invaluable ecosystems.
Nestle’s Use of Satellite Imagery
Nestlé is using cutting-edge satellite imagery to enhance its Global Reforestation Program. Their Global Reforestation Program see’s Nestle aiming to plant and grow 200 million trees globally by 2030. By monitoring over 150,000 shade trees in coffee farms with high-resolution images, Nestlé ensures better sunlight regulation and increased productivity while reducing carbon emissions.
As satellites offer detailed insights into Earth’s surface features, Nestlé can make informed decisions for future reforestation projects. With Nestle aiming to combat climate change and achieve its 2050 net zero emissions goal. By leveraging advanced satellite technology, Nestlé is pioneering innovative solutions for environmental sustainability.
Take Action Today!
The use of high-resolution satellite imagery in reforestation is a game-changer. It provides a cost-effective and efficient solution to the challenges of reforestation, offering detailed insights that can guide conservation efforts.Take action with Arlula and power the critical decisions in reforestation efforts. From aiding in the planning of reforestation projects to monitoring their success or utilising EO data management tools to pinpoint areas of greatest concern, satellite imagery is invaluable to develop actionable change. Learn more about Arlula’s satellite imagery and EO data solutions today.
Common Questions
Want to keep up-to-date?
Follow us on social media or sign up to our newsletter to keep up to date with new product releases and case studies.




